Mastering Prompts
As is common with people, clear communication is incredibly important to relay specific intent for a product or goal. People practice clear communication often with each other, but less so with computers. Until now we have been accustomed to limiting our “communication” with computers to that of a search inquiry on Google. When working on other applications within the computer or coding we often use instructions or commands to direct what the computer should do and what the output should be. In most of these situations, we have a firm understanding of what to expect as an output. With AI this all changes.
When communicating with AI we are not providing commands. We may provide some basic instruction, but not in as concise a manner as described above. Instead, we now treat the AI-enabled computer as a competent, intelligent, widely-read partner who can engage in conversation and brainstorming activities. Just like in a real conversation, dialog begins with a conversational prompt. When we communicate with AI we use prompts to assist or encourage it to respond. The tone, clarity, length and specifics of the prompt will greatly determine the response received. Just like in real life, clarity is key.
They are input elements such as words, phrases, questions, or keywords that users enter into AI tools to generate results. These prompts are the instructions or discussion topics users provide for the AI model to respond to. It can take the form of a question, statement, or any stimulus aimed at fostering creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Firstly, when using AI tools, the better your prompts, the better the results you’ll get. Simply put, an effective prompt sets the topic and provides clear instructions on the task, effectively guiding the AI tool. Is it challenging to write a good prompt? Sometimes. The quality of the output relies on the specificity and clarity of the prompts or input instructions.
Remember, you always have multiple attempts to craft the desired AI output. If your first prompt does not provide what you are looking for, respond again with another addition to your initial prompt. This approach could be described as a process of trial and error.
- Formulate a relevant prompt.
- Consider when the output falls short of expectations.
- Enhance the clarity of the prompt. You could refine your prompts using exemplars, such as the ones in the prompt library.
- Repeat the process
Remember that as you chat with AI, the model will learn more about what you need. Use the conversation to help AI improve its outputs.
Head to the next tab where you can apply some principles of good prompt writing.
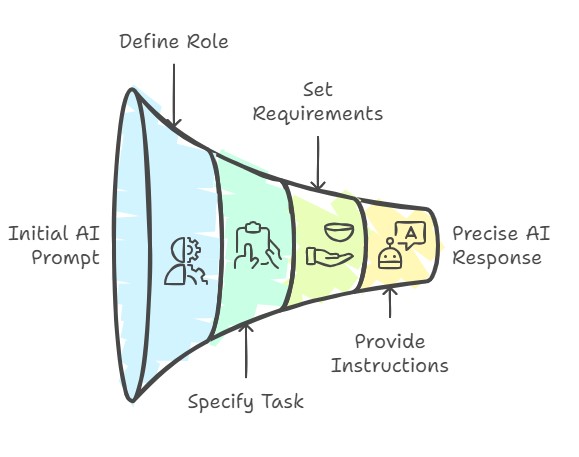
Follow the 4 elements in the table below for some basic tools to help start making great prompts for your AI inquiries.
| Element | Description | Prompt |
| Role | Prompts starting with “act as…” or “pretend to be…” will provide responses similar to that of the role that you provide. Setting a specific role for a given prompt increases the likelihood of more accurate information when done appropriately. | “You are an expert in business information systems tutoring.” |
| Task | The task is a summary of what you want the prompt to do. A lot of creativity comes into writing a great task. It can range from generating birthday gift ideas to doing game show questions with the content from your last lecture. | “I want to study the following topics: customer relationship management systems, information security and privacy, and business process management.” |
| Requirements | Writing clear requirements is all about giving as much information as possible to ensure your response doesn’t use any incorrect assumptions. AI models make assumptions about any information they don’t have in the prompt | “Ask me questions that integrate ideas from these three topics. After you ask each question, wait for my response. Then you should respond but do not tell me the answer. Instead, ask me questions and use the Socratic questioning approach to help me arrive at the answer myself.” |
| Instructions | Instructions will inform the AI how to complete the task. Instructions can include examples of how it is supposed to work, steps it can follow, or any information. | “First analyze each of the three topic areas, review the requirements of the task, then consider some unique and engaging ways to question me.” |
